The IoT has been gaining popularity for a long time. It is a frightening future for some people, but for others, it is a familiar present. It seems like an unnecessary extravagance for some businesses, while for others, it is becoming the best initiative they have ever taken. For some countries, it is already working and actively expanding, and for others, it is not even going to be implemented yet. Well, let's take a closer look at what the IoT is? How does the IoT work? And in particular, how can the IoT change transportation and logistics?
What is the IoT?
The Internet of Things is a relatively young phenomenon for which there is not yet a single definition, a single global standard, or even an established attitude.
On the one hand, the Internet of Things is a large and complex concept that we are just beginning to realize. Its essence is the constant connection of physical objects to the network and constant sharing of data about its state or the external space. This concept aims to optimize and automate the work of all infrastructures, the objects of which are connected to the network.
On the other hand, the Internet of Things is a set of technologies that enable constant connectivity and data transfer between physical objects, from hardware like sensors and modems to software in services and applications. Many of them exist and are in active use in smart homes, giant factories, global shipping, and so on.
We at Mad Devs provide comprehensive IoT solutions for businesses of all sizes and complexities, so our customers get a lot more data about how their infrastructure works, how to improve and protect it, increase the efficiency of operations, and monitor it in real-time. For example, the developed traffic intersection monitoring system for company CityCam.
Despite the amazing technology we are developing and using, we cannot fully realize the ultimate concept of the IoT. Not all objects around us are smart yet. For example, if streetlights and CCTV cameras are not connected to the cloud, the streetlights will not adjust the light based on camera data, and the cameras will not turn on night mode if the streetlights are off. More precisely, they will do so on a schedule or with their built-in sensors, but not based on data from each other. But the more technology we develop for this, the better it performs, and the more the need for it arises - the closer we get to implementing this concept of the future world. The world where every piece of infrastructure of an entire city, state, and even planet is constantly exchanging data with each other to make our lives easier, better, cleaner, and safer. Let it be more like a technological evolution rather than a revolution.
How does IoT work?
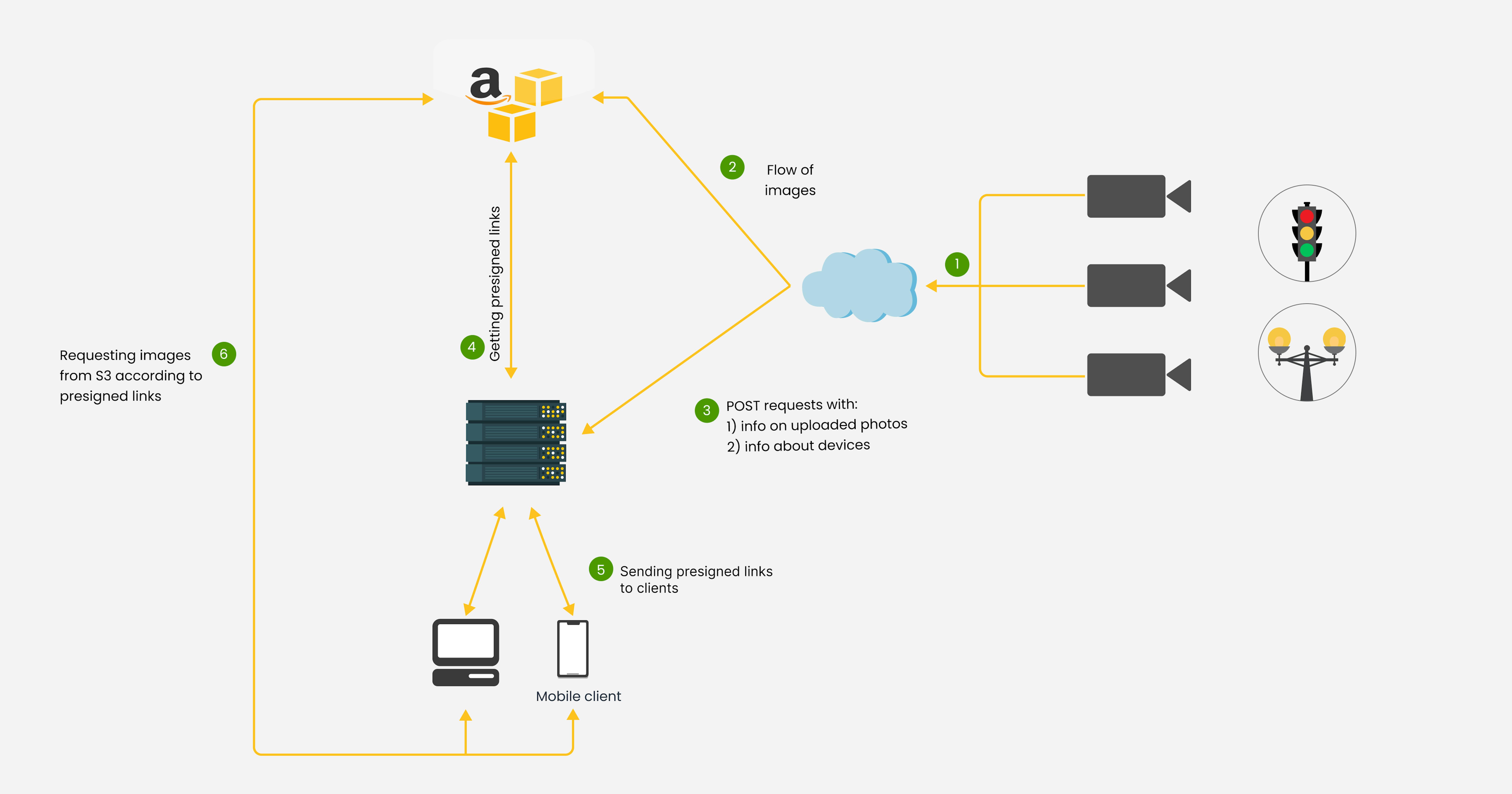
- First, data from sensors on each device is sent to its server. The own server is needed to have single access to data from all devices and able to communicate with these devices.
- The data from this server is sent to the cloud, which is technically also a server, but allows for large and complex calculations with data as quickly as possible because the capacity of those servers is much higher. For example, AWS.
- In the cloud, in depth data analysis or real time data analysis take place, from which you can improve the performance of the system or draw valuable conclusions about how it works and what it's aimed at.
- The analysed data is sent to own server. If the server has specific models of operations prescribed to receive a certain data, the server sends a command to the deviсes.
- Upon receiving commands, IoT devices execute the specified actions. These actions could range from adjusting the temperature in a smart home system to triggering a process on industrial machinery.
- Subsequently, data regarding the execution of these commands is gathered and relayed back to the server, perpetuating this cycle. This cyclical process allows the IoT system to learn and fine-tune its performance based on continuous data analysis.
Of course, some initial data collection and analysis is required, which identifies fundamental problems in the system's operation and helps find the best way to operate it. After that, data collection allows you to monitor the system's proper operation and all of its components and improve upon the methods previously found.
For example, a smart home first needs to determine what time you usually get home from work so that the coffee machine has time to make you fresh coffee. And only after that, if the coffee has time to cool down and you manually start the coffee maker again, you can conclude that you need to start making coffee 5 minutes before you come in, not 10.
Or first, you need to calculate the operating model of the equipment in the factory, in which one machine will work on a part after the other and will not interfere with each other. And only then reduce the intervals between their operations to a minimum and speed up the whole work process.
That's why any IoT network requires professional developers. We have sensors, high-speed internet, and clouds to store and analyze big data with AI. But these are all means to build a smart system, the creation, and configuration of which requires excellent experience of developers in each case. Here at Mad Devs, we have developers with vast experience in development and a great desire to make the world a better place through promising new technologies.
Why is IoT getting more popular?
IoT and the benefit
The main reason, as usual, is economic. Let's face it, a lot of great technology was invented years ago, but it cost a lot more to implement and use than to profit from it. The same is valid here. Modems and sensors have recently become cheap enough to manufacture and small enough to fit everywhere.
Now the cost of such components can be less than a dollar. Their size has become so small that they can be built anywhere. And their power is more than enough to share large amounts of data at high speed.
IoT and 5G
The spread of 4G and 5G networks has also been a vital boost. Of course, there was the mobile Internet before, but it wasn't fast enough or widely accessible sufficient for the Internet of Things. At least not if we're not talking about smart homes, but large infrastructures like cities or transportation.
Wireless Internet speeds are now so fast that sending, analyzing, and receiving large amounts of data is done in real-time, almost without delay. And there are fewer and fewer areas with no Internet coverage at all.
IoT and AI
Last but not least is the excellent progress in artificial intelligence and machine learning. It is worth recognizing that cheap electronics and fast Internet are just a way of collecting and sharing data, but all the magic happens in processing them. Machine learning models do in moments what humans would do manually for days, months, or even years, or maybe not at all. So it is a credit to artificial intelligence and machine learning, without which the Internet of Things is hard to imagine at all, to create systems that work, optimize and regulate them in real-time.
📖 Discover how AI is revolutionizing the transportation industry, enhancing safety, efficiency, and sustainability in our new article "Transportation and AI: The Next Level of Autonomous System"
How is IoT used in transportation and logistics?
As mentioned earlier, the IoT can be used anywhere, and it probably will be used everywhere very soon. However, there are industries where it is a desirable initiative, and there are industries where it is becoming a necessary practice. The IoT is increasingly becoming a necessity in the transportation and logistics industry. There are many reasons for this, but let's look at the main ones.
Reasons
More and more people are moving from rural areas to cities. It has been happening at a breakneck pace over the past 50 years. Even the global pandemic has not fundamentally changed this trend. As more and more people move to cities, so more equipment is needed to help deal with the increased strain on city infrastructure. At the same time, people stay at home more and shop online more often. It creates an additional load on the city's infrastructure at the expense of delivery services and makes significant changes in intercity trucking, through which products are delivered.
It's also worth recognizing that humanity has polluted the planet lately. The IoT can optimize the transportation system not only to bring material benefits but also to reduce the harm it causes. Optimization makes it possible to calculate the shortest routes for cargo delivery, optimize the fuel supply to the engine, and prevent accidents with fuel spills into the environment, for example, when we are talking about cargo ships.
Hardware
Temperature sensors can be helpful in a vast number of situations. Of course, in a pandemic, the first thing that comes to mind is installing them in surveillance cameras, especially in the case of public transportation. However, it can be handy for taking temperature readings from vehicle components. In conjunction with readings from other sensors, you can adjust the fuel supply, turn on the cooling system, and regulate many aspects of the vehicle's operation.
Gyroscopes, accelerometers, and proximity sensors don't just help our smartphones track the number of steps in a day and so on. They are some of the main sensors whose data can be used in the transportation system to track traffic, eliminate traffic jams, prevent accidents, create an optimal route, monitor the proper performance of the vehicle's internal components, etc. Of course, first, we think about autopilot in electric cars and robotics. But such things as magnetometers, humidity, and pressure sensors also help predict the weather, current sea behavior, reef proximity, and many critical points for shipping.
Image and acoustic sensors are not just for government surveillance or terrorist detection. Video and audio data provide the most valuable and broad set of data from which amazing things can be done. For example, using computer vision technology to detect and identify physical objects. For example, you can quickly identify the company employees and not turn on the starter when another person tries to get behind the wheel. Or track a driver's face and voice and keep him from falling asleep at the wheel. Or detect a deer or a fallen tree on the highway a few hundred meters away, which the human eye can hardly do. The use of such data is an extensive area of research, with breakthroughs occurring every day, and such sensors will improve transportation business and logistics in a vast number of ways.
These are the simplest and most popular sensors, but the data they can provide is invaluable, and machine learning algorithms do miracles with them. More sophisticated sensors have integrated processors and modems, such as RFID sensors. Such sensors require minimal power consumption, are more resilient in the absence of a network between devices, and can send data themselves. This can be useful in urgent situations. For example, for detecting gas leaks, there are gas RFID sensors that can take immediate action regardless of the Internet connection.
Key points
Knowing what the Internet of Things is, how it works and how it can be used, let's highlight the main benefits it can provide.
Increased comfort. The Internet of Things allows maximum infrastructure automation, from the home coffee machine to the parking lot and the entire highway. And all of this happens behind a screen for the average city dweller, who simply enjoys seeing how much is done without his or her involvement.
Increased safety. Sensors can detect anything much faster than humans, and machine learning algorithms can consider an impossible number of factors and instantly make the right decision. It sounds a little scary, but the IoT is doing a much better this job than any of us.
Efficiency gains. Yes, this is where humans lose out, too. When you have to analyze an extensive system and improve its efficiency by considering many factors, it will be complicated for a human. Besides, the system has to be constantly improved, and the data has to be processed in real-time. Only a machine can do that, and machines do it very well.
Improving the environment. As stated earlier, the IoT not only takes care of people but also takes care of nature. Logistics and transportation companies are not only looking for ways to reduce costs but also to reduce fuel use, carbon footprint, and all sorts of options to prevent accidents with fuel being released into the environment. And it is worth admitting that quite a large number of companies guarantee a reduction in these figures of 10 even up to 20 percent, which is a good result.
Summary about IoT
Future possibilities
It all sounds too good to be true. It sounds like a magic pill that cures all diseases.
We at Mad Devs know digital transformation very well, working with a lot of data and using modern technology. And from ourselves, we can confidently say that it requires a cautious approach in the development and integration of such technologies, but having done everything right, it works and brings excellent results.
And from all appearances, the Internet of Things will spread more and more intensely and penetrate deeper into our lives. For some, it is a fashion trend, for others a way to improve comfort, for others to increase production efficiency, and for others, a way to save the planet and make people's lives better.
Even if everyone has his interest, but when there are new companies providing services in this area, and new technologies make this area necessary and helpful—that's good news. Almost all objects around us will likely be connected to the network and soon work for the common good.
Risks and scares
Risks and scares arise when we are not talking about private companies and their technology but the IoT's government or even global systems. Such a system would be gigantic, and its complexity would be unimaginable. Therefore, errors in its operation will be inevitable, and the more we rely on it, the more dire the consequences of those errors will be. Therefore, implementing this system at such a high level requires careful legislative regulation and development of technologies for it, the chance of failure of which is close to zero. Otherwise, we will be even less protected from total surveillance, mass hacker attacks, and other terrible things than now. The solution could be to move to a decentralized Internet and more sophisticated protocols for transmitting and storing data.












