Analyze with AI
Get AI-powered insights from this Mad Devs article:
Blockchain technology is steadily reshaping the banking industry, offering financial institutions a path to greater transparency, efficiency, and security. Initially seen as the backbone of cryptocurrencies, blockchain has evolved into a powerful tool with transformative potential for traditional banking.
In this article, we explore blockchain's role in banking, its opportunities, challenges, and the long-term implications for the financial sector.
Why banks are turning to blockchain
As highlighted in our article "Digital Transformation in Banking and Financial Services," the financial sector is at the forefront of adopting innovative technologies, and blockchain is no exception. Moreover, the global blockchain technology market size is expected to reach around USD 1,879.30 billion by 2034.
Starting in 2025, banks across North America, Europe, and Asia will embark on live trials of digital asset and currency transactions over the Swift network, indicating a move towards integrating blockchain technology. But what challenges in the banking sector have pushed this technology to the forefront?
Key challenges driving blockchain adoption in banking
- Inefficient payment systems — Traditional cross-border transactions are slow, expensive, and reliant on intermediaries, often taking several days to process.
- Fraud and security concerns — The centralized nature of legacy banking systems makes them vulnerable to fraud, hacking, and data breaches.
- Lack of transparency — Conventional banking processes often lack transparency, leading to mistrust among customers and partners.
- Strict regulatory compliance — Banks face increasing pressure to meet complex regulatory requirements.
- High operational costs — Legacy systems are costly to maintain and prone to inefficiencies.
Why blockchain is the solution
Blockchain's core attributes—decentralization, immutability, and real-time data synchronization—make it an ideal solution for banks aiming to enhance operations and customer experiences.
- Problem: Inefficient payment systems
Blockchain's real-time data synchronization eliminates delays, reduces costs, and enhances transparency in global payments.
- Problem: Fraud and security concerns
Blockchain's decentralized and immutable ledger ensures enhanced security and minimizes fraud risks.
- Problem: Lack of transparency
Blockchain offers a transparent and tamper-proof ledger, improving trust and accountability.
- Problem: Regulatory compliance
Blockchain's traceability and automated smart contracts simplify compliance by providing a clear, auditable record of transactions.
- Problem: High operational costs
Blockchain reduces overhead by streamlining processes, cutting out intermediaries, and automating repetitive tasks through smart contracts.
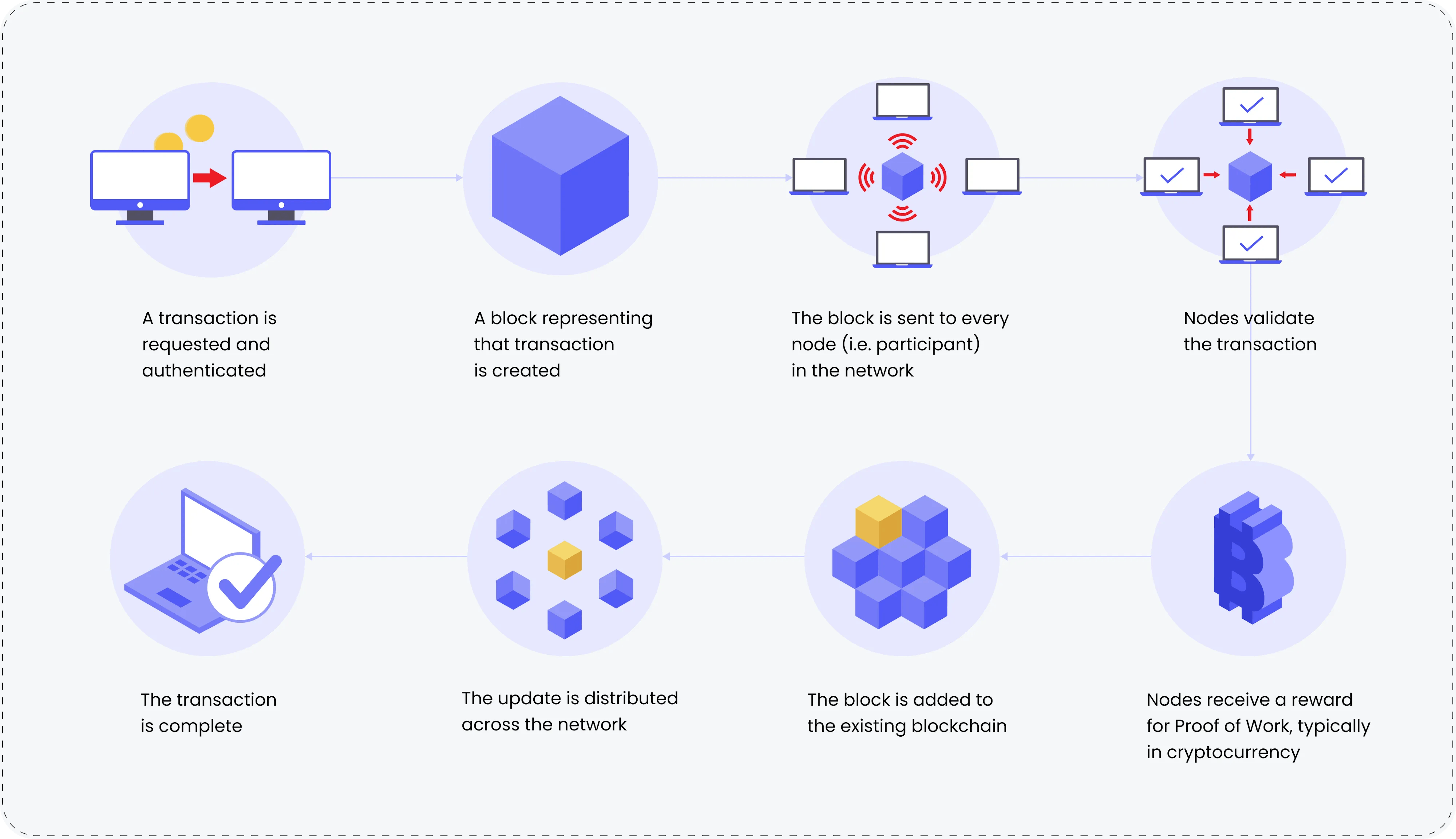
Advantages and disadvantages of blockchain in banking
Blockchain technology has emerged as a transformative force within the banking sector, offering financial institutions an opportunity to enhance operational efficiency, reduce fraud, and improve customer satisfaction. However, while the advantages are compelling, the adoption of blockchain comes with its own set of challenges. Let's delve deeper into this topic and examine both sides of the question.
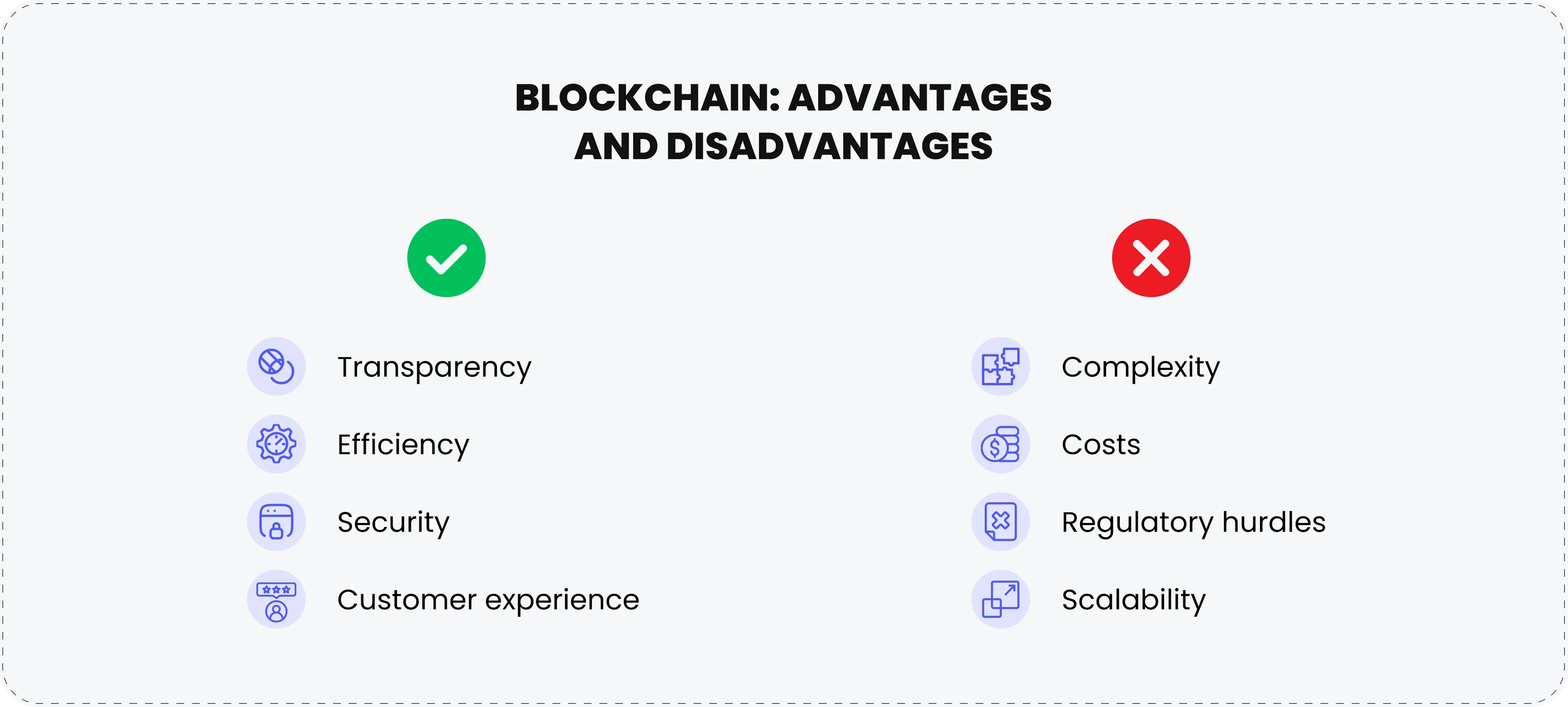
Advantages of blockchain in banking
1. Transparency
Blockchain's distributed ledger system ensures that all participants have access to the same immutable record of transactions. This not only reduces the risk of fraud but also builds trust among stakeholders by improving accountability across the banking ecosystem. Transparency in operations enhances regulatory compliance and simplifies auditing processes.2. Efficiency
Blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries in financial transactions, such as clearinghouses or correspondent banks. This streamlines processes, reduces transaction times from days to seconds, and lowers operational costs. For instance, cross-border payments, which traditionally take several days, can now be processed almost instantaneously using blockchain technology.3. Security
The combination of cryptographic algorithms and decentralized architecture makes blockchain inherently secure. Transactions are encrypted, and data is stored across multiple nodes, making it highly resistant to hacking and unauthorized alterations. Even if one node is compromised, the rest of the network remains unaffected, ensuring data integrity and reliability.
📄 Moreover, blockchain aligns with key industry standards and regulations, which further bolsters its security adoption. For example:
- ISO/IEC 27001 Compliance
Blockchain's inherent security features, such as encryption and decentralized storage, help organizations implement robust Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). This alignment ensures compliance with ISO/IEC 27001 standards for managing sensitive information securely.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
While blockchain's immutability can pose challenges for GDPR compliance, careful design—such as encrypting personal data and off-chain storage—allows organizations to meet the EU's data privacy requirements. This ensures transparency, accountability, and the protection of user rights.
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
Blockchain can support secure payment processes by encrypting transaction data and reducing reliance on intermediaries. When integrated correctly, it helps meet PCI DSS standards for protecting payment card information.
- AML and KYC Regulations
Blockchain's transparency and traceability simplify compliance with AML and KYC regulations. Immutable records allow financial institutions to monitor transactions, detect anomalies, and verify customer identities effectively.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
In healthcare, blockchain ensures secure and tamper-proof storage of patient records, supporting compliance with HIPAA's standards for data privacy and security.
4. Customer experience
Blockchain simplifies complex banking procedures, reducing wait times and paperwork for customers. Automated processes like smart contracts ensure faster services, such as loan approvals and payment settlements. The result is a smoother, more efficient banking experience, boosting customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Disadvantages of blockchain in banking
1. Complexity
Implementing blockchain in banking requires specialized knowledge and technical expertise. From selecting the right blockchain platform to integrating it with existing systems, the process can be daunting. Banks must invest in training and hiring skilled professionals, which can delay adoption.2. Costs
The initial investment for developing and deploying blockchain solutions is substantial. Costs include infrastructure setup, software development, regulatory compliance, and ongoing maintenance. While long-term savings are a potential benefit, the upfront expenses can deter smaller institutions from adopting blockchain.3. Regulatory hurdles
The regulatory environment for blockchain is still evolving, with significant variations across regions. Adapting to these dynamic requirements, such as anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) standards, can be challenging. Compliance issues may slow down adoption and require constant updates to ensure legality.4. Scalability
Blockchain networks, especially public ones, often struggle to handle large transaction volumes efficiently. Congestion can lead to slower processing times and higher costs during peak periods. For financial institutions managing millions of transactions daily, this remains a critical challenge that requires scalable solutions.
Despite these challenges, blockchain's transformative capabilities present numerous opportunities for the banking sector. Let's discuss them.
Opportunities for blockchain in banking
Blockchain offers myriad opportunities to streamline banking operations and create new revenue streams:
✔ Accelerated payments and settlements
Blockchain significantly reduces the time and cost associated with cross-border transactions. Banks can process payments in seconds instead of days by eliminating intermediaries and enabling real-time data synchronization.
Major banks are already experimenting with blockchain-powered payment platforms to provide real-time settlements:
JPMorgan has developed Kinexys, a suite of blockchain-based solutions aimed at revolutionizing financial transactions. Kinexys offers services such as Digital Payments, which facilitate near real-time, cross-border transactions, and Digital Assets, enabling the tokenization of assets for greater utility. These innovations have processed over $1.5 trillion in transactions, demonstrating significant scalability and reliability.
Bank of America is advancing its digital strategy by integrating blockchain and AI technologies to enhance its financial services. The bank has filed numerous blockchain-related patents, indicating a commitment to leveraging this technology for improved transaction efficiency and security. While specific project details are proprietary, the bank's focus includes streamlining interbank transfers and cross-border payments.
Deutsche Bank is collaborating with industry partners to address blockchain interoperability challenges. The bank contributed to a comprehensive How Financial Institutions Navigate a Multichain World white paper discussing how financial institutions can navigate a multichain world, emphasizing the need for interlinked network models that embrace multiple blockchains. This initiative aims to enhance accessibility and liquidity for tokenized assets.
UBS has successfully piloted a blockchain-based payment system called UBS Digital Cash to enhance the efficiency of cross-border transactions. The pilot included domestic transactions within Switzerland and cross-border payments in various currencies, including U.S. dollars, Swiss francs, euros, and Chinese yuan. This initiative aims to provide more efficient and transparent cross-border payments, allowing firms to better manage intraday liquidity.
Citi has launched the Citi Integrated Digital Assets Platform (CIDAP), leveraging blockchain technology to develop secure, efficient, and innovative digital asset solutions. CIDAP offers services such as Citi Token Services for Cash and Trade, providing clients with instant payment capabilities and 24/7 liquidity transfers between Citi branches. These solutions aim to streamline processes and enhance asset utilization and mobility.
These initiatives reflect a broader industry trend toward adopting blockchain technology to improve efficiency, security, and transparency in the banking sector.
✔ Automated smart contracts
Smart contracts streamline complex processes like loan disbursements, insurance claims, and trade finance. By automating compliance checks and eliminating manual oversight, banks can cut operational costs and reduce processing times. For instance, in trade finance, smart contracts ensure that payments are automatically released once predefined conditions are met, improving efficiency and reducing risks.
✔ Enhanced fraud prevention
With its immutable and transparent ledger, blockchain acts as a powerful deterrent against financial fraud. Banks can track every transaction in real-time, reducing risks of money laundering, unauthorized alterations, and duplicate records. This aligns with AML (Anti-Money Laundering) efforts, providing regulators and financial institutions with better oversight and more robust audit trails.
✔ Asset tokenization for investment opportunities
Blockchain enables the tokenization of assets such as real estate, commodities, and bonds, breaking them into smaller, tradable units. This creates opportunities for fractional ownership, allowing retail investors to participate in previously inaccessible markets. For example, tokenizing a high-value property enables multiple investors to own a share, unlocking new avenues for portfolio diversification and liquidity.
✔ Seamless identity verification
Traditional identity verification processes, such as Know Your Customer (KYC), are often time-consuming, taking days or even weeks to complete. Blockchain-based identity systems offer a secure and decentralized solution, allowing customers to control and share their data with multiple institutions without repetitive procedures. This reduces onboarding times to minutes while enhancing data privacy and security. For instance, once a customer's identity is verified on a blockchain, they can seamlessly share it with other banks or services, streamlining the process across the ecosystem.
Challenges of implementing blockchain in banking
While blockchain technology holds significant potential for revolutionizing the banking sector, its integration is not without challenges. Recent insights, including those highlighted in this Reuters article, suggest that skepticism toward both cryptocurrencies and blockchain remains prevalent among bankers and clients alike. This cautious stance adds another layer of complexity to adoption.
Here are the main challenges:
Regulatory uncertainty
Blockchain operates in a complex legal landscape. Variations in regulations across jurisdictions make it challenging for banks to ensure compliance, especially with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements.
Scalability issues
Blockchain networks often struggle with scalability, especially during peak transaction volumes. This can lead to delays and higher costs, undermining its efficiency.
Integration with legacy systems
Banks rely on decades-old infrastructure, and integrating blockchain with these legacy systems is a technical and financial hurdle.
High initial costs
The development and deployment of blockchain solutions require substantial investment. For smaller banks, this can be a significant barrier to entry.
Lack of expertise
Blockchain is a relatively new technology, and there is a shortage of skilled professionals who can design, implement, and maintain these systems.
As the Reuters article suggests, skepticism within the banking industry is unlikely to dissipate overnight even with expected regulatory easing. For blockchain to gain broader acceptance, stakeholders must address these challenges collaboratively while building trust and understanding of its capabilities.
The future of banking with blockchain
The future of blockchain in banking is not about replacing traditional banking systems but about enhancing and transforming them. As blockchain technology matures, its integration into banking operations will likely follow a path of coexistence, collaboration, and innovation. Here's what the future holds:
1. Coexistence with traditional banking
Blockchain will complement, not replace, existing banking systems. Traditional banks will adopt blockchain for specific use cases where it adds value, such as cross-border payments, trade finance, and fraud prevention. Banks will leverage blockchain's strengths while maintaining core operations on conventional systems to ensure reliability and regulatory compliance.
2. Widespread use of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Central banks globally are exploring blockchain-based CBDCs to modernize monetary systems. These digital currencies aim to enhance payment systems, reduce cash dependency, and provide a secure and efficient alternative to traditional fiat currencies. For example:
- China's Digital Yuan has already entered advanced pilot stages.
- The European Central Bank and other institutions are actively researching blockchain solutions for CBDCs.
3. Cross-border payments
Blockchain technology is poised to eliminate the inefficiencies of cross-border payments, reducing costs and settlement times significantly. Future advancements may result in near-instant global payments with minimal fees.
- Platforms like Ripple and JPMorgan's Kinexys already demonstrate the potential for blockchain-based solutions to streamline international transactions.
4. Evolution of trade finance
Trade finance is a natural fit for blockchain due to its complexity and reliance on trust among multiple parties. Blockchain can digitize and automate trade documents, improve supply chain transparency, and reduce processing times. For instance:
- IBM's We.Trade and HSBC's Contour are blockchain platforms transforming trade finance.
5. Enhanced security and fraud prevention
Blockchain's immutability and transparency will play a critical role in reducing financial fraud. Future banking systems will use blockchain for secure identity verification, transaction authentication, and fraud detection, making banks more resilient against cyber threats.
6. Smart contracts for automation
Smart contracts will gain wider adoption in automating banking processes. These self-executing contracts can simplify loan disbursements, insurance claims, and compliance monitoring. For instance:
- Loans could be automatically disbursed once predefined conditions, such as credit checks, are met.
- Trade agreements can be executed automatically upon delivery verification.
7. Tokenization of Real-World Assets (RWA)
The tokenization of RWA, such as real estate, stocks, or commodities, will unlock new investment opportunities. Blockchain enables fractional ownership, making high-value assets accessible to a broader audience. Banks will play a central role in facilitating these tokenized transactions, creating new revenue streams.
8. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) collaboration
Banks may increasingly adopt or integrate decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols. This hybrid approach could allow them to offer innovative financial products such as blockchain-based lending, borrowing, and staking while ensuring regulatory compliance and customer protection.
9. Regulatory and standardization developments
As blockchain adoption grows, regulatory frameworks will become more robust. Governments and financial authorities will work to standardize blockchain protocols, ensuring security, transparency, and compliance across the banking sector.
Unlock blockchain's potential in banking with Mad Devs
Blockchain technology is reshaping the banking landscape, offering innovative solutions to age-old challenges. By embracing blockchain, financial institutions can unlock unparalleled efficiency, security, and customer satisfaction. As the industry evolves, those adopting blockchain will be at the forefront of the next wave of banking transformation.
At Mad Devs, we deeply understand the unique challenges and transformative opportunities blockchain brings to the finance industry. Our expertise, highlighted in the Hinkal Protocol Case, highlights our ability to create innovative and tailored blockchain solutions that address real-world problems. This project underscores our commitment to user data privacy, implementing advanced features to ensure confidentiality while delivering seamless and secure systems.
Contact us today for a free consultation and discover how we can help revolutionize your banking systems with secure, efficient, and scalable blockchain technology.











